VideoNavQA: Bridging the Gap between Visual and Embodied Question Answering
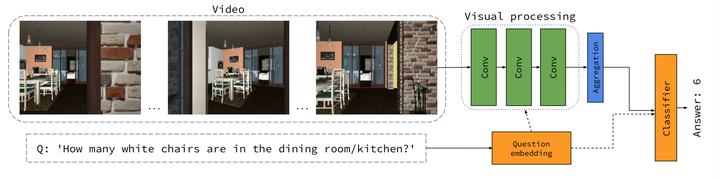 High-level overview of the VideoNavQA task and our proposed approach.
High-level overview of the VideoNavQA task and our proposed approach.Abstract
Embodied Question Answering (EQA) is a recently proposed task, where an agent is placed in a rich 3D environment and must act based solely on its egocentric input to answer a given question. The desired outcome is that the agent learns to combine capabilities such as scene understanding, navigation and language understanding in order to perform complex reasoning in the visual world. However, initial advancements combining standard vision and language methods with imitation and reinforcement learning algorithms have shown EQA might be too complex and challenging for these techniques. In order to investigate the feasibility of EQA-type tasks, we build the VideoNavQA dataset that contains pairs of questions and videos generated in the House3D environment. The goal of this dataset is to assess question-answering performance from nearly-ideal navigation paths, while considering a much more complete variety of questions than current instantiations of the EQA task. We investigate several models, adapted from popular VQA methods, on our benchmark. This establishes an initial understanding of how well VQA-style methods can perform within the novel EQA paradigm.